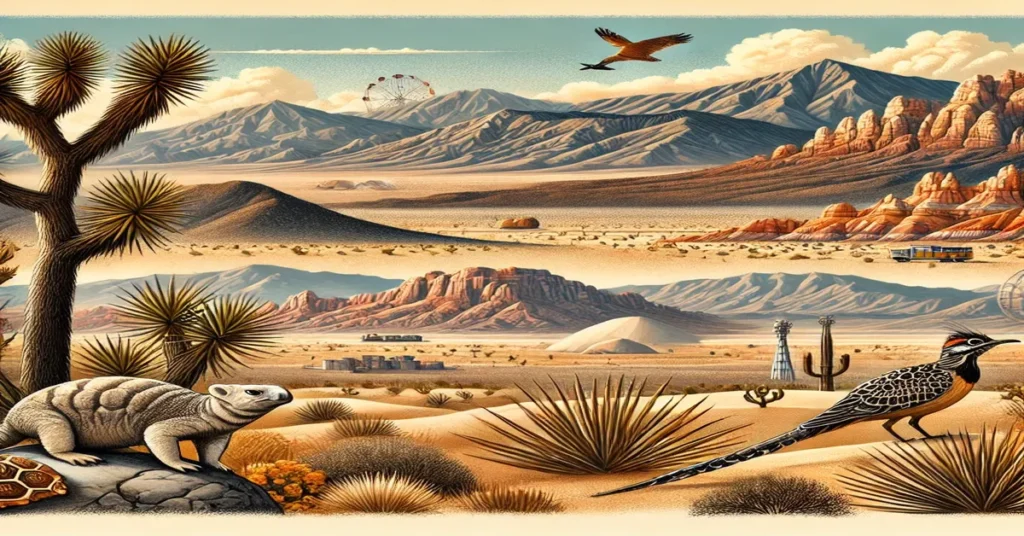
The Mojave Desert, or “Sa Mạc Mojave” in Vietnamese, is one of the most captivating landscapes in the United States. Spanning parts of California, Nevada, Arizona, and Utah, this desert is known for its stark beauty, unique wildlife, and fascinating geological features. Covering an area of approximately 47,877 square miles, the Mojave Desert is often called the “high desert” due to its higher elevation compared to neighboring deserts like the Sonoran and Great Basin. This desert is home to the iconic Joshua Tree, the hottest recorded place on Earth, Death Valley, and a variety of plant and animal species adapted to its arid environment.
This article provides a comprehensive guide to the Mojave Desert, exploring its geography, climate, plant and animal life, as well as major attractions and recreational activities. Whether you’re an adventurer, a nature enthusiast, or simply curious about desert ecosystems, this guide will help you appreciate the Mojave Desert’s unique charm.
Understanding the Geography of the Mojave Desert
The sa mạc mojave Desert is located in the southwestern United States and is bordered by three other major deserts: the Sonoran Desert to the south, the Great Basin Desert to the north, and the Colorado Plateau to the east. It lies primarily within southeastern California, but it also extends into southern Nevada, northwestern Arizona, and southwestern Utah.
The Mojave Desert is characterized by its high elevation, with most of the desert sitting above 2,000 feet (610 meters) above sea level. The terrain includes rugged mountains, vast plains, and valleys. The highest point in the Mojave Desert is Charleston Peak in Nevada, which reaches an elevation of 11,916 feet (3,632 meters). In contrast, the lowest point is found in Death Valley, which lies 282 feet (86 meters) below sea level and holds the record for the hottest temperature ever recorded on Earth.
This desert is known for its unique landforms, including sand dunes, dry lake beds (playas), and volcanic features. Some well-known geological formations in the Mojave Desert include the Kelso Dunes, Zabriskie Point, and the Ubehebe Crater. The Mojave River, a mostly dry river that flows underground for much of its length, also plays a significant role in shaping the desert’s landscape.
Climate of the Mojave Desert
The Mojave Desert has an arid climate with extremely hot summers, mild winters, and low annual rainfall. The climate can be classified as a hot desert climate, with average high temperatures in summer reaching 100°F (38°C) or higher, and winter temperatures averaging around 60°F to 70°F (15°C to 21°C). However, temperatures can vary greatly depending on elevation and location within the desert.
Seasons in the Mojave Desert:
- Summer (June to August): Summers are extremely hot, especially in areas like Death Valley, where temperatures can soar above 120°F (49°C). This period is also very dry, with minimal rainfall.
- Fall (September to November): Fall brings slightly cooler temperatures, making it a more comfortable time to explore the desert. It’s also the start of the prime tourist season.
- Winter (December to February): Winters are mild, with temperatures in the low 60s°F (15°C) during the day and colder temperatures at night. The winter season can bring occasional rainfall, though it is usually light.
- Spring (March to May): Spring is one of the best times to visit the Mojave Desert, as temperatures are moderate, and the desert landscape often comes alive with blooming wildflowers after the winter rains.
Rainfall in the Mojave Desert is sparse, averaging only 3 to 5 inches (76 to 127 millimeters) annually. This desert also experiences strong winds, particularly during the spring months. These conditions make the Mojave Desert an extreme yet fascinating place to explore.
Flora of the Mojave Desert
Despite its harsh environment, the Mojave Desert is home to a surprising variety of plant life. The flora in this region has adapted to survive in the arid climate, extreme temperatures, and low water availability. Some of the most iconic plants in the Mojave Desert include:
- Joshua Tree (Yucca brevifolia):
- The Joshua Tree is perhaps the most famous plant in the Mojave Desert and serves as its unofficial symbol. These unique, twisted trees grow in higher elevations and can reach heights of up to 40 feet (12 meters). They are protected within Joshua Tree National Park.
- Creosote Bush (Larrea tridentata):
- The creosote bush is one of the most common plants in the Mojave Desert. It has adapted to the arid climate with deep roots and waxy leaves, which help it retain moisture. It is known for its resilience and can live for thousands of years.
- Mojave Yucca (Yucca schidigera):
- The Mojave yucca is a hardy plant found throughout the desert. Its sharp, spiky leaves and tall flower stalks make it easy to recognize. The plant has long roots that reach deep underground to access water.
- Desert Holly (Atriplex hymenelytra):
- This small, salt-tolerant shrub has silver-gray leaves that help reflect sunlight and conserve water. It is commonly found in alkaline soils, such as those in salt flats and playas.
- Brittlebush (Encelia farinosa):
- Known for its bright yellow flowers that bloom in the spring, brittlebush is a common sight in the Mojave Desert. It is highly drought-tolerant and provides food for desert wildlife.
During spring, if there has been sufficient winter rainfall, the desert is often blanketed with vibrant wildflowers, including desert marigold, poppies, and sand verbena. This annual bloom attracts visitors and photographers from around the world.
Fauna of the Mojave Desert
The sa mạc mojave Desert is home to a diverse range of wildlife species, many of which are specially adapted to survive in the harsh desert environment. Some of the most notable animals include:
- Desert Tortoise (Gopherus agassizii):
- The desert tortoise is an iconic species in the Mojave Desert and is well adapted to its dry conditions. These slow-moving reptiles dig burrows to escape the heat and can live up to 80 years. The desert tortoise is a threatened species and is protected under federal law.
- Mojave Rattlesnake (Crotalus scutulatus):
- The Mojave rattlesnake is one of the most venomous snakes in North America. It is known for its distinctive diamond pattern and is commonly found in desert habitats. This snake is a skilled predator, feeding on rodents and small animals.
- Bighorn Sheep (Ovis canadensis nelsoni):
- Bighorn sheep are often seen navigating the rocky hillsides of the Mojave Desert. Their strong legs and hooves allow them to traverse steep and rugged terrain with ease. They are known for their impressive, curved horns.
- Coyote (Canis latrans):
- The adaptable coyote thrives in the Mojave Desert. Coyotes are omnivorous and can survive on a diet of small animals, plants, and even carrion. They are commonly spotted throughout the desert.
- Roadrunner (Geococcyx californianus):
- The roadrunner, a bird known for its speed and adaptability, is commonly found in the Mojave Desert. These birds are known for their unique appearance and diet, which includes insects, small reptiles, and even venomous snakes.
- Kangaroo Rat (Dipodomys spp.):
- The kangaroo rat is a small, nocturnal rodent that has adapted to desert life by obtaining all its water needs from the seeds it eats. It is named for its large hind legs, which allow it to jump great distances.
Many of these animals have developed specialized adaptations to conserve water, avoid heat, and find food in an environment where resources are scarce.
Major Attractions in the Mojave Desert
The Mojave Desert offers a variety of attractions for visitors, from national parks and protected wilderness areas to historic sites and quirky roadside stops. Here are some of the must-visit attractions:
- Death Valley National Park:
- One of the most famous destinations in the sa mạc mojave Desert, Death Valley is known for its extreme temperatures, unique landscapes, and otherworldly beauty. Key attractions include Badwater Basin, Zabriskie Point, Mesquite Flat Sand Dunes, and Dante’s View.
- Joshua Tree National Park:
- Located at the intersection of the sa mạc mojave and Colorado Deserts, Joshua Tree National Park is known for its unique Joshua Trees, impressive rock formations, and scenic trails. The park offers excellent opportunities for rock climbing, stargazing, and photography.
- Mojave National Preserve:
- This vast preserve encompasses a wide range of landscapes, from sand dunes and volcanic formations to canyons and Joshua Tree forests. Highlights include the Kelso Dunes, Hole-in-the-Wall, and Cima Dome.
- Red Rock Canyon National Conservation Area:
- Located near Las Vegas, Nevada, Red Rock Canyon features stunning red sandstone formations, scenic driving routes, and hiking trails. It’s a popular destination for both locals and tourists.
- Calico Ghost Town:
- Calico is a restored 19th-century silver mining town that offers a glimpse into the Mojave Desert’s mining history. Visitors can explore historic buildings, shops, and participate in activities like panning for gold.
- Route 66:
- The famous Route 66 crosses through parts of the sa mạc mojave Desert. Travelers can experience nostalgic roadside attractions, quirky shops, and scenic desert views along this historic highway.
- Amboy Crater:
- Amboy Crater is a dormant volcanic cinder cone located along Route 66. Visitors can hike to the top of the crater and enjoy panoramic views of the surrounding desert landscape.
- Kelso Depot:
- This historic train depot, located in Mojave National Preserve, has been restored and now serves as a visitor center with exhibits on the history and ecology of the Mojave Desert.
Conclusion
The sa mạc mojave Desert is a land of extremes, offering a diverse array of landscapes, unique plant and animal life, and fascinating attractions. From the scorching heat of Death Valley to the enchanting Joshua Tree National Park, the sa mạc mojave Desert invites visitors to explore and experience its rugged beauty. Whether you’re interested in hiking, wildlife watching, stargazing, or simply enjoying the stark beauty of the desert, the Mojave has something to offer.
As you plan your visit, make sure to prepare for the desert’s extreme conditions, stay hydrated, and respect the natural environment. The Mojave Desert is a precious ecosystem that requires responsible tourism to preserve its beauty for future generations.
FAQs
- What is the best time to visit the Mojave Desert?
- The best time to visit is during the fall and spring when temperatures are mild and comfortable for outdoor activities.
- Are there any dangerous animals in the Mojave Desert?
- The Mojave Desert is home to animals like rattlesnakes and scorpions. Always stay vigilant and avoid disturbing wildlife.
- Can you camp in the Mojave Desert?
- Yes, there are many designated campgrounds in places like Mojave National Preserve and Joshua Tree National Park.
- What should I bring when visiting the Mojave Desert?
- Bring plenty of water, sunscreen, a hat, protective clothing, and a map. The desert’s conditions can be extreme.
- How hot does Death Valley get in summer?
- Death Valley is one of the hottest places on Earth, with summer temperatures often exceeding 120°F (49°C).
- Is the Mojave Desert the same as Joshua Tree National Park?
- Joshua Tree National Park is part of the Mojave Desert, but it also includes areas of the Colorado Desert.